Author: Valentina Prgomet Member of the AmCham IPR Task Force, Legal and Enforcement Manager for Balkan countries at React Balkan
*The article in Macedonian language, published by Kapital can be found at the bottom of this page.
Many innovations are the result of years of research, and significant investments of various resources are involved in their development, with the goal of gaining financial reward for these inventions through licenses or sales. The creator of the innovation, or the holder of the intellectual property rights (IPR), has the exclusive right to use their intellectual property and/or to transfer the right to use it via copyright licenses to others. Therefore, intellectual property rights hold economic value just like any other property.
In the context of globalization, strengthening and establishing a robust and secure global trading system supports local distributors and consumers. One of the fundamental purposes of IPR is to encourage rights holders to bring their ideas into various markets, thereby supporting creators’ rights. Consequently, strong IPR protection gives businesses the confidence to enter foreign markets. With robust measures in place, businesses can more easily choose investment destinations, expecting quality protection for their IPR.
Unfortunately, international trade in counterfeit products remains one of the biggest challenges in this area. To better understand how this type of trade operates in our region, and to underscore the importance of preventing and sanctioning it, this text analyzes the Balkan route of trade in counterfeit products.
The Movement of Counterfeit Products through the Balkans
Balkan countries are rapidly growing economies and legislation across these countries is being continuously modified to comply with EU legislation. All regional countries have similar and on paper strong legal frameworks, but issues still arise when it comes to dealing with counterfeit goods. Sometimes, due to the lack of resources, in other cases lack of efficient mechanisms for implementing regulations and right holders limited IP strategy.
Exploring the Balkan route, results show that the Balkans are lush grounds for trade over maritime and land distribution (and manufacture). Having a vast geographical location, the Balkans are connected to other continents and regions, subsequently Extended Balkan route is created.
Case studies (source React case management), which feature the regional countries picture the form of the analysis on the Balkan route for counterfeit goods.
As a transit country, North Macedonia plays a role in the movement of goods, including counterfeit products. Companies distribute and sell their goods in North Macedonia through merchants, wholesalers, and retailers (both online and offline). The retail sector in North Macedonia is dominated by small shops, a few shopping malls, and foreign supermarket chains.

Goods mostly arrive through land, but also through air channels. Less seen, but indeed present, is also transport through port channels in the neighboring countries.
As a starting point, counterfeit goods are sent from China or Türkiye. Then follow transport through Greece, with destination Kosovo, North Macedonia, or Bosnia and Herzegovina (Arizona Market). In most cases, Greek customs detain the illicit goods and provide details for the route of the subject transport.
From the South side, goods mostly come from Dimitrov grad Bulgaria to Serbia where they are stopped before they enter the Serbian local market. Along the central Mediterranean, Montenegro sets grounds for counterfeit goods entering the market, mostly by air. Based on the case studies, Türkiye and China are most notorious for the transport of counterfeits in the Balkans.
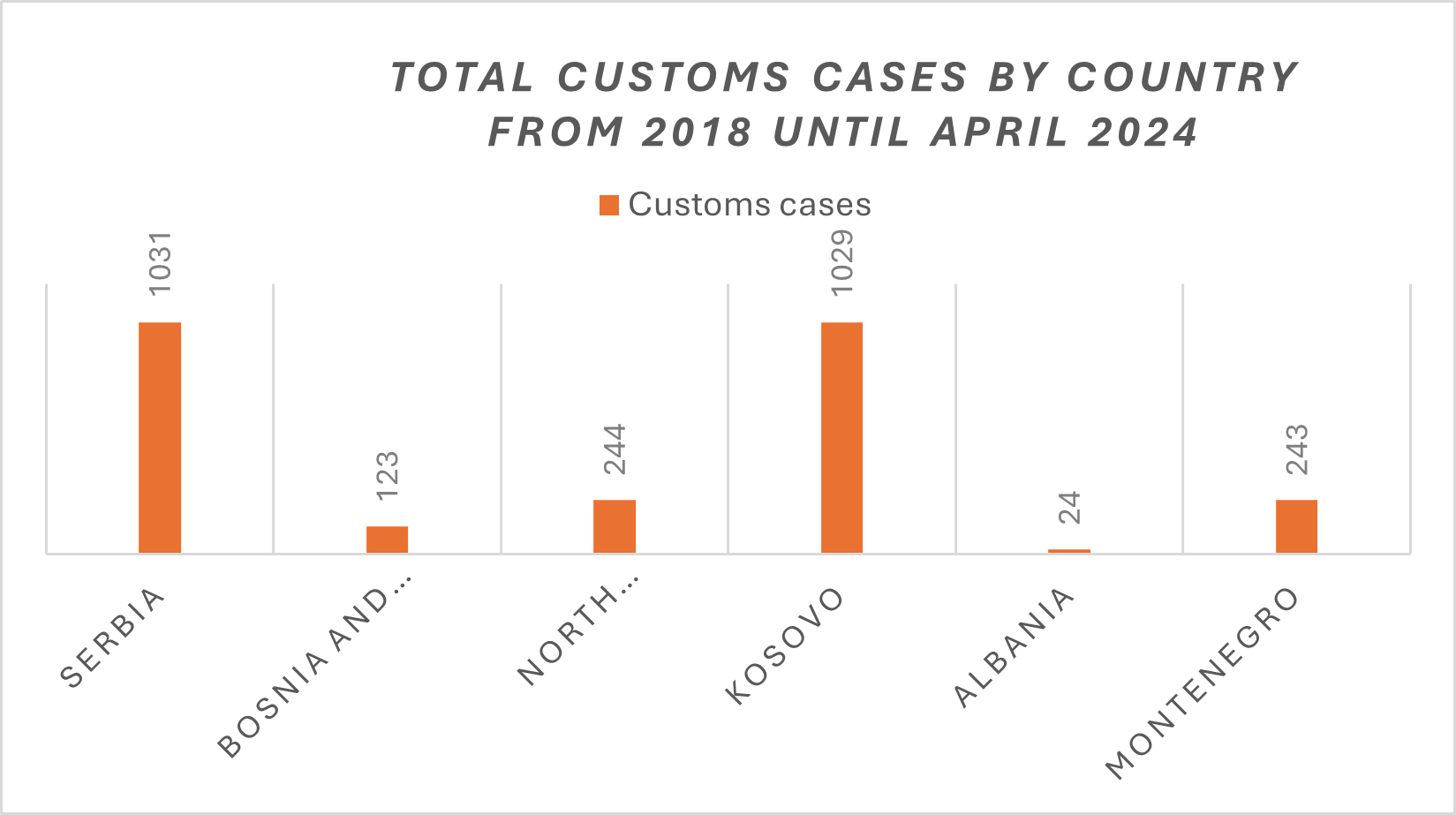
Regional Statistics (source React case management)
Total customs cases by country from 2018 until April 2024:
– Albania: 24 cases
– Bosnia and Herzegovina: 123 cases
– Kosovo: 1029 cases
– Macedonia: 244 cases
– Montenegro: 243 cases – Serbia: 1031 cases
Synergy Between Rights Holders and Authorities is Key to Effective Protection of Intellectual Property at the Borders
Border measures enable holders of IPR to obtain protection of their trademarks. Involvement & support from IPR holders to customs authorities is essential. Hence, cooperation between authorities & IPR holders is the key to success.
Together with the authorities, the participation and backing of rights holders are vital for stronger IPR protection. Both parties (institutions and rights holders) create a symbiotic relationship that signals to infringers that when IPR are violated a robust enforcement mechanism is in place.
IP holders should reinforce their anti-counterfeiting policies for smaller markets and smaller quantities and authorities should intensify efforts with not only clear infringements but to change policies with parallel imports and online sales for more effective results in IPR protection.

